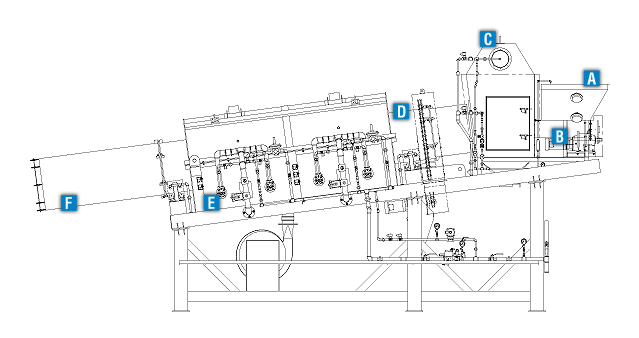
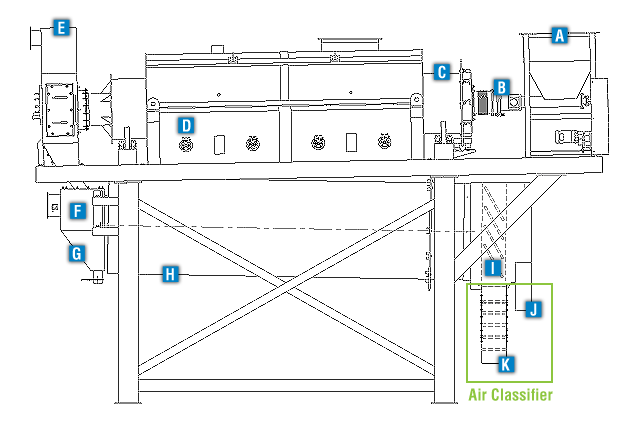
EnviroAir Carbon Reactivation Systems are used to reactivate spent activated carbon that has absorbed moisture and organic compounds. EnviroAir will also provide the required air quality control equipment to ensure compliance with EPA and local air quality control standards.
EnviroAir Carbon Reactivation Systems Feature:
- Indirectly heated – no flame impingement on the carbon to cause oxidation and loss of carbon material
- Exhausts are collected and discharged directly into air quality system – reducing pollutants
- Fully automatic system – simple to operate
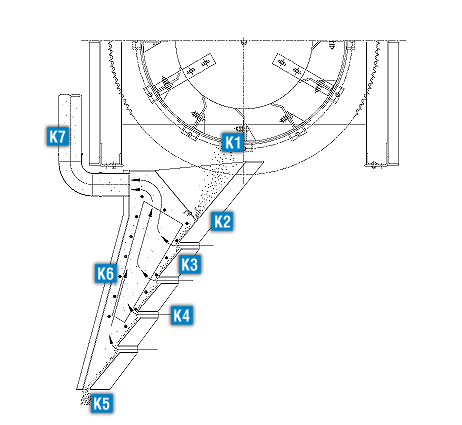
Carbon Reactivation Process Diagram
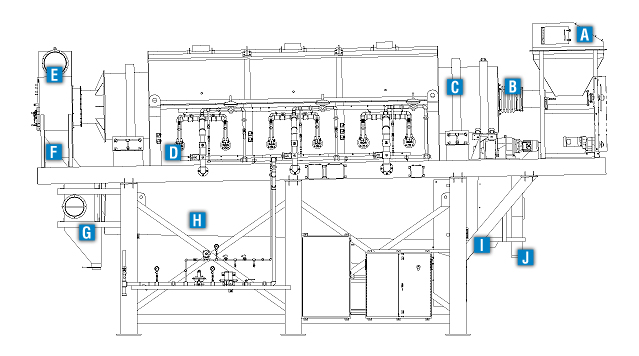
Spent carbon is fed into the input hopper.
Sealed screw feeder feeds the spent carbon into the rotary retort at a constant rate.
Spent carbon is heated to 1,400 to 1,650°F inside the rotary retort, evaporating moisture and oxidizing volatile organic compounds absorbed in the carbon micropores.
Gas-fired burners heat the retort from the outside. This indirect heat prevents flame impingement on the carbon that could cause oxidation and loss of the carbon material.
Retort exhaust gases are collected in the retort exhaust hood and discharged to an air quality control system.
Transfer Chute
Cooling air is collected in the cooling drum exhaust hood and discharged to an air quality control system.
Heat from the reactivated carbon is transferred to the cooling air, in the rotary cooling drum. The reactivated carbon leaves the cooling drum at no more than 30°F above ambient temperature.
Fines in the reactivated carbon are filtered through screened openings in the rotary cooling drum.
Reactivated carbon is discharged from the cooling drum.
- Spent carbon is fed into the input hopper.
- Sealed screw feeder feeds the spent carbon into the rotary retort at a constant rate.
- Spent carbon is heated to 1,400 to 1,650°F inside the rotary retort, evaporating moisture and oxidizing volatile organic compounds absorbed in the carbon micropores.
- Gas-fired burners heat the retort from the outside. This indirect heat prevents flame impingement on the carbon that could cause oxidation and loss of the carbon material.
- Retort exhaust gases are collected in the retort exhaust hood and discharged to an air quality control system.
- Transfer Chute
- Cooling air is collected in the cooling drum exhaust hood and discharged to an air quality control system.
- Heat from the reactivated carbon is transferred to the cooling air, in the rotary cooling drum. The reactivated carbon leaves the cooling drum at no more than 30°F above ambient temperature.
- Fines in the reactivated carbon are filtered through screened openings in the rotary cooling drum.
- Reactivated carbon is discharged from the cooling drum.